System and surroundings in thermodynamics
A system of thermodynamics can be defined as a matter or region on which analysis is done. The system is separated from surrounding by the boundary. Everything external to the system is surrounding. System and surroundings in thermodynamics together is called a universe.
System and surroundings in thermodynamics
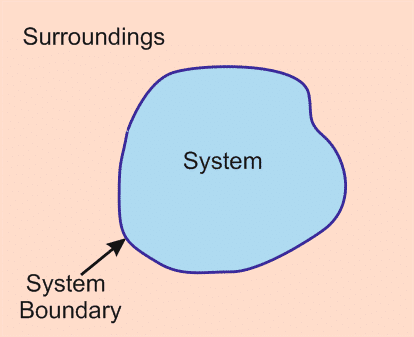
- System: Any matter or region which is focused.
- Surrounding: Everything except the system is surrounding
- Boundary: It separates the system and surrounding. It can be fixed or movable.
Fixed boundary example: a rigid box containing gas
Movable boundary example: a cylinder with a piston
Types of system
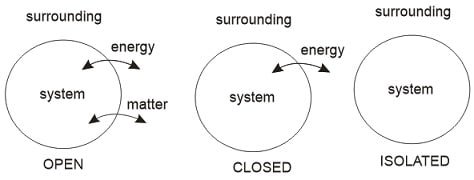
- Open system: Both energy and mass transfer across the boundary is possible
Example: Turbine, pump, compressor
- Closed system: Only energy taser is possible across the boundary
Example: Piston cylinder without valves
- Isolated system: Energy or mass transfer is not possible across the boundary.
Example: Thermos flask
Property of system
In thermodynamics, properties are point function and are exact differentials
- Point function: Does not depends on path history
Example: Temperature, pressure, volume
- Path function: Depends on the path history
Example: Work, heat
- Intensive properties: Independent of mass
Example: Pressure, temperature, density, specific volume, specific heat
Note: All specific properties are intensive properties.
- Extensive properties: Dependent on mass
Example: Volume, energy, heat capacity, enthalpy
Process
- Reversible process
A process when reversed in direction, follows the same path as that of the forward path without leaving any effect on the system and surrounds in thermodynamics is called reversible process.
Example: A frictionless quasi-static process is called a reversible process.
- Irreversible process
The process which is not reversible means it does not follow the same path when reversed is called irreversible process.
Example: all actual process are irreversible process.
This is all about system and surroundings in thermodynamics.



I have read so many articles or reviews concerning the blogger lovers except this post is truly
a nice piece of writing, keep it kaos polos built up surabaya
I was suggested this web site by my cousin. I am not sure whether this
post is written by him as no one else know such detailed about my trouble.
You are wonderful! Thanks!