Calorific value formula and types of calorific value
Calorific value is defined as amount of energy generated by combustion of specific amount of food or fuel. Calorific value unit is joule per kilogram or calorie per kilogram.
There are two types of calorific value
- Higher calorific value ( HCV )
- Lower calorific value ( LCV)
Higher calorific value is also known as gross calorific value. (GCV)
Lower calorific value is also known as net calorific value (NCV)
Higher calorific value or Gross calorific value
When 1 kg of fuel is burned, product of combustion is cooled down to room temperature. Heat obtained by this complete combustion is known as higher calorific value.
Lower calorific value or Net calorific value
When 1 kg of fuel is burned, heat obtained by this combustion is known as lower calorific value or net calorific value. Here product of combustion is not cooled down to room temperature, steam generated during combustion is not condensed and heat carried away by combustion is not recovered.

Calorific value formula
Calorific value of the fuel is calculated using bomb calorimeter. Here crucible of bomb calorimeter is filled with fuel for which calorific value is required. Then it is ignited. Surrounding water initial and final temperature is recorded.
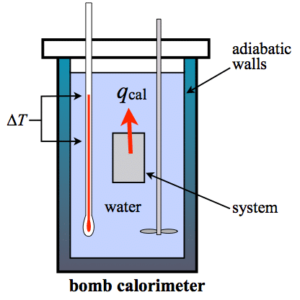
Heat given away by the fuel = heat gained by water
Q1 = Q2
m1 * CV = m2 * specific heat of water * (T2-T1)
For example, let us calculate specific heat of fuel
for 100 gm fuel and 2 kg water, temperature difference recorded is 5 degree
Calorific value of fuel = (mass of water*specific heat of water*temp ) /fuel mass
Calorific value of fuel = (2*4.186*5)/0.1 = 418 kJ/kg



bookmarked!!, I really like your blog!