What is degree of freedom in mechanics?
When a link is connected to one or more other links, it imposes a restriction on the relative motion of the combined link or mechanism. This number of restrictions may vary according to the type of link and connection they made with each other. Basically, there are 3 transitional and 3 rotational motions are considered. So the degree of freedom in mechanics can be defined as the number which is resulted after deducting a number of restriction from 6.
Degree of freedom = 6 – number of restrains
Here, the number of restrains can never be zero for any joint. It is only possible in case of the independent link.
If the number of restrains becomes 6 then the mechanism is rigid as there is no provision for any relative movement.
Degree of freedom in mechanics
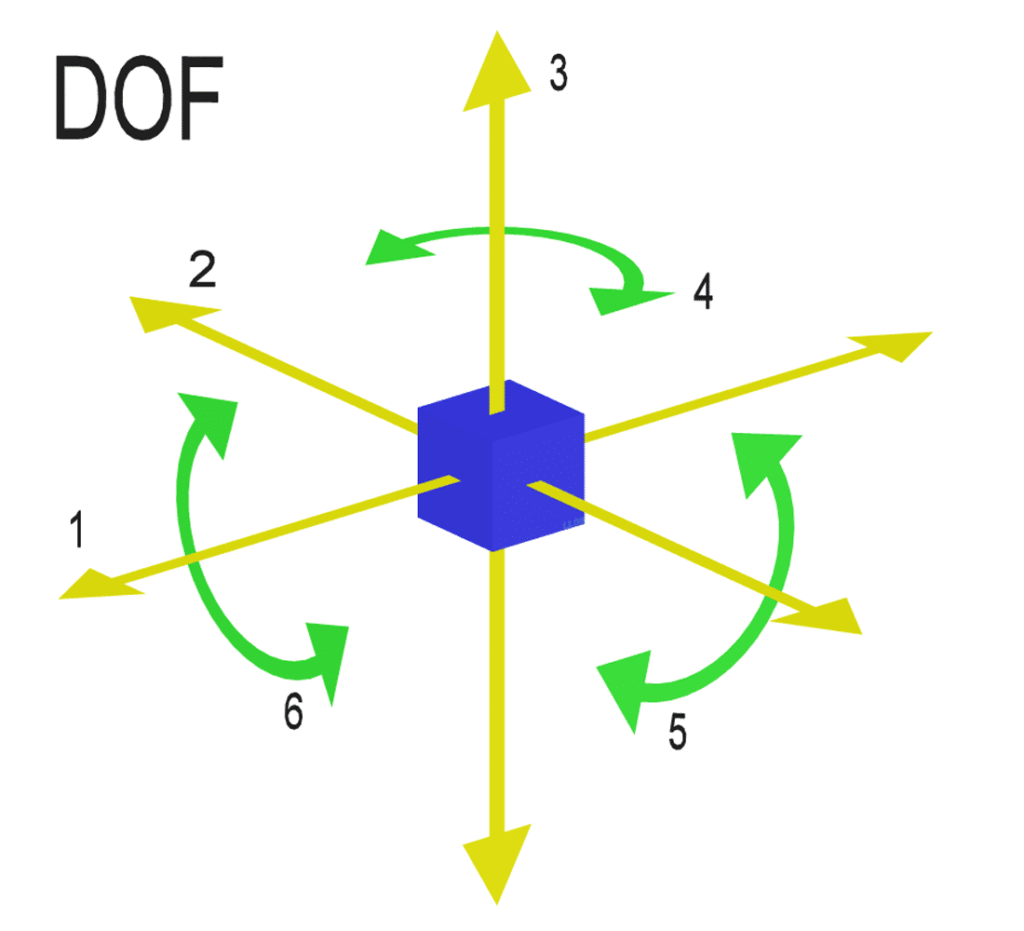
Degree of freedom of space mechanism (3D)
F= 6(L-1) – 5P1 – 4P2 – 3P3 – 2P4 – P5
Degree of freedom of plane (2D): Grabbler’s Criterion
F= 3(L-1) – 2P1 – P2
where F is D.O.F.
- L is number of links in a mechanism
- P1 is number of pairs having DOF =1
- P2 is number of pairs having DOF =2
- P3 is number of pairs having DOF =3
- P4 is number of pairs having DOF =4
- P5 is number of pairs having DOF =5
Kutzback’s equation
F= 3(L-1) -2j – h
L is number of links
j is number of binary joints
h is number of higher pairs
Grubbler’s equation
For those mechanisms which have DOF = 1 and h=0
3l – 2j -4 = 0
l = number of links
j = number of binary joints
If DOF = 0 : Frame
DOF < 0 : Redundant frame
DOF > 0 : Constrained or unconstrained frame
Also read: Types of restrictions/constraints in mechanics
This is all about the degree of freedom in mechanics.
Note: All mechanism have minimum 4 numbers of links


